Unveiling the Perils: Windows Server Default Password and Their Implications
- Home
- Support
- Tips System Rescue
- Unveiling the Perils: Windows Server Default Password and Their Implications
Summary
Discover the risks of default passwords in Windows Server, as well as vulnerabilities. Learn how to conduct security audits and guard against brute-force attacks. Find the Windows Server default password here.
Table of contents
Windows Server Default Passwords: Ensuring the Security of Your System
In today’s digital age, protecting sensitive information is of utmost importance. When it comes to Windows Server, one of the key steps to securing your system is setting a strong password. However, many users may be unaware that Windows Server comes with a default password out-of-the-box. This default password poses a significant security risk, as it can be easily exploited by cybercriminals. In this article, we will explore the implications of using the default password and provide essential guidelines on how to change it to safeguard your server against potential threats.
Default administrator usernames and passwords are a common security vulnerability in Windows Server. Many manufacturers ship their servers with default login credentials, which are often not changed by users. This makes it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access to the server and compromise its security.
Here are some examples of default administrator usernames and passwords for different server brands:
- Cisco servers often have a default username of “admin” and a default password of “admin”.
- D-Link servers commonly have a default username of “admin” and a default password of “Admin”.
- Crystalview servers have a default username of “Admin” and a default password of “Crystal”.
- Cyberguard firewalls have a default username of “cgadmin” and a default password of “cgadmin”.
- Dell servers may have default usernames and passwords such as “admin” and “admin” or “root” and “calvin”, depending on the specific model.
It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list, and default usernames and passwords may vary for different server models and manufacturers.
| Brand Name | Default Admin UserName | Default Admin Password |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco | admin | admin |
| D-Link | admin | Admin |
| Crystalview | Admin | Crystal |
| Cyberguard | cgadmin | cgadmin |
| Dell | admin | admin |
| Dell | root | calvin |
| 3Com | admin | Admin |
| Belkin | admin | admin |
| BenQ | admin | Admin |
| D-Link | admin | Admin |
| Digicom | admin | Michelangelo |
| Linksys | admin | Admin |
| Netgear | admin | password |
| Sitecom | sitecom | Admin |
| Asus | admin | admin |
| Synology | admin | Admin |
| Arris | admin | password |
| Apple iphoneIOS4.X | root | alpine |
| DELL | admin | password |
| Huawei ADSL2+ | admin | admin |
| Netcomm | admin | password |
| Netstar | admin | password |
| SAMSUNG | none | none |
| Sigma | admin | password |
| SUN | admin | admin |
| Com21 | admin | admin |
| Comersus | admin | dmr99 |
| Compaq | Administrator | admin |
| Compaq | Console | Administrator |
| Compaq | dc770t | none |
| Compaq | Insight Manager | none |
| Compaq | Insight Manager | anonymous |
| Compaq | Insight Manager | PFCUser |
| Compaq | Management Agents | administrator |
| Compaq | PC BIOS | none |
| Compualynx | administrator | asecret |
| Compualynx | SCM | administrator |
By promptly changing the default administrator username and password and following best practices for password security, server administrators can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect the Windows Server from potential threats.
One common issue faced by Windows Server users is forgetting the default Admin password. This can be a significant security concern as it leaves the system vulnerable to unauthorized access. Fortunately, there are ways to change the default Admin password, and one effective tool for this task is Renee PassNow.
To begin with, users must download and install Renee PassNow on a separate computer, as it requires a different machine to create a bootable media. Once installed, follow these step-by-step instructions to change the default Admin password:
Step 1: Download and Install Renee PassNow
Start by downloading Renee PassNow from the official website and install it on a different computer that you can access. You can choose the appropriate version based on your computer’s operating system.

Remove Windows Login Password 3 steps for whole password remove process.
Recover the files Recover the deleted files without Windows system.
Transfer the data Transfer the important files of the computer with system.
Multifuctional Data transfer, data recovery, bootable problem recovery can be run without system.
Highly compatible Windows 11/10/8.1/8/7/XP/Vista. UEFI boot.
Remove Login Password Support Windows 11/10/8.1/8/7/XP/Vista. UEFI boot.
Recover the files Recover the deleted files without Windows system.
Transfer the data Transfer the important files of the computer with system.
Step 2: Create a Bootable USB or CD/DVD
Launch Renee PassNow and insert a USB flash drive or blank CD/DVD into the computer. Select the option to create a bootable media. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
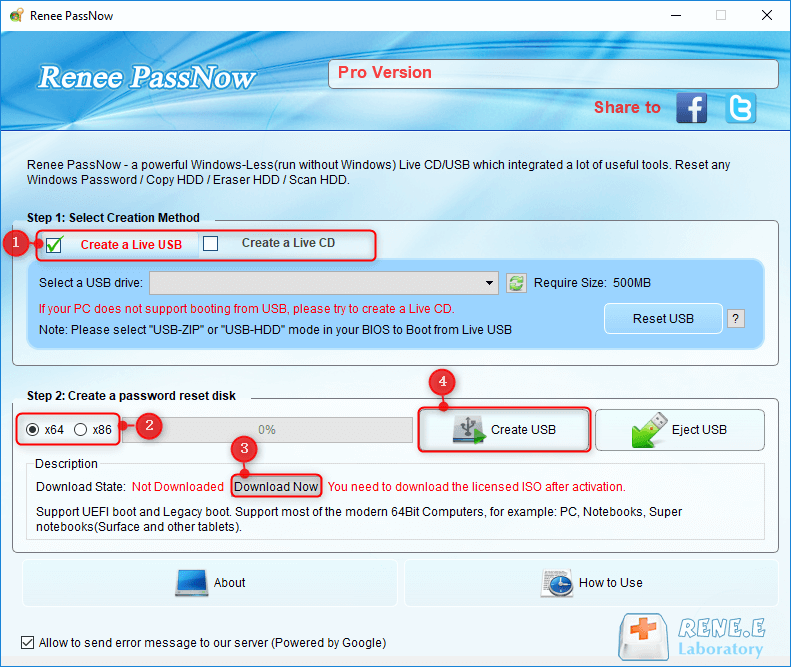
Step 3: Boot the Locked Server from the Bootable Media
Insert the bootable USB or CD/DVD into the locked Windows Server computer. Restart the computer and enter the BIOS settings by pressing the appropriate key (usually F2 or Delete). Configure the boot order to prioritize the bootable media.

Step 4: Reset the Password
After successfully booting from the bootable media, Renee PassNow will load. Select “PassNow!” function after booting from the new created Windows password reset disk.
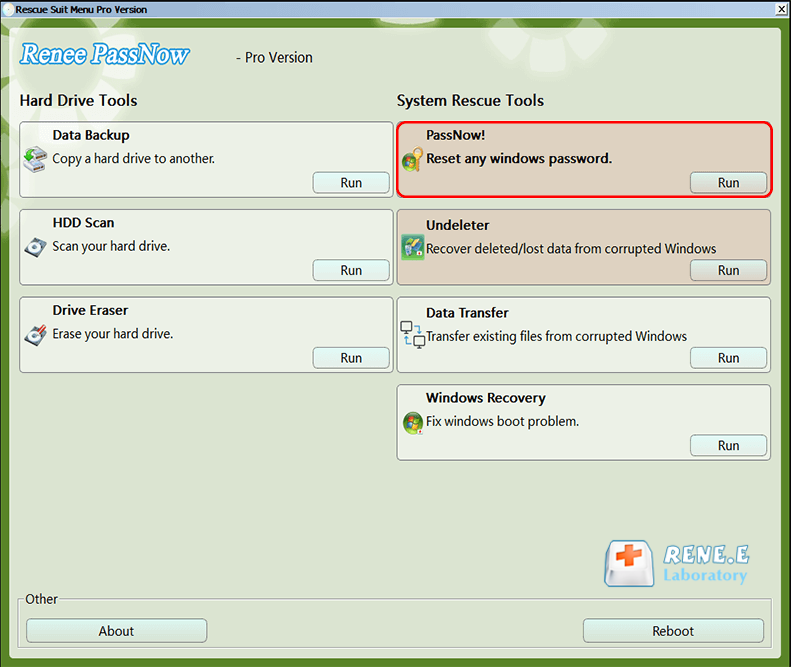
Step 5: Resetting the Password
Choose the user account for which you want to reset the password. Then, click on the “Reset” button. Renee PassNow will remove or reset the password for the selected user account.
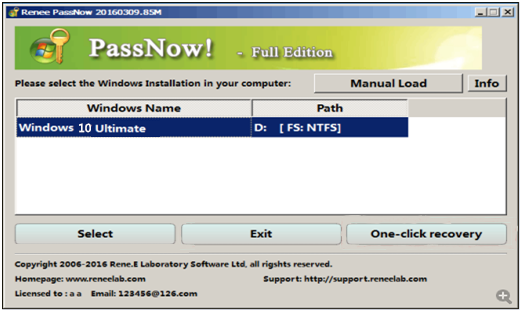
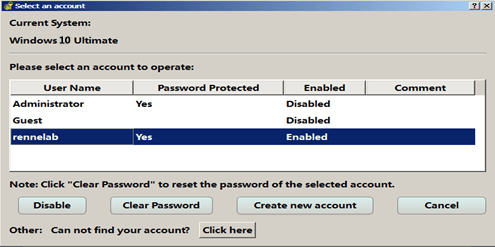
Step 6: Reboot the Server
Once the password is reset, remove the bootable media from the server and restart the computer. You will now be able to log in to Windows Server without a password.
Step 7: Create a New Password (Optional)
After logging into Windows Server 2019, it is recommended to create a new password for security purposes. Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete on your keyboard and select “Change a password” option.
Following these steps will allow users to change the default Admin password on their Windows Server installations even if the original password is forgotten. Remember to choose a strong and unique password to enhance the security of your system.
To conduct a security audit for default passwords on Windows Server installations, there are several steps that can be followed to ensure a thorough assessment and address potential vulnerabilities.
1. Identify all Windows Server installations: Begin by compiling a list of all Windows Server installations within your network. This can be done by scanning your network using network discovery tools or by referring to existing network documentation.
2. Determine default administrator credentials: Once you have identified the Windows Server installations, research the default administrator username and password for each brand or model. This information can usually be found in the product documentation or on the manufacturer’s website.
3. Create a testing environment: Set up a testing environment where you can safely assess the default password vulnerabilities without affecting the live server environment. This can be done by virtualizing the Windows Server installations using virtualization software. In particular, whether it is possible for people to easily access the SAM file that stores account and password information.
4. Use security auditing tools: Utilize password auditing tools or scripts specifically designed for assessing default passwords. These tools often come with a set of preconfigured default passwords that they can test against the servers.
| Product Name | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Atera | A SaaS platform for managed service providers with remote monitoring and management tools. Includes a reporting facility for system audit reports. | Contact for pricing |
| ManageEngine Log360 | A SIEM package that collects logs from network endpoints and cloud platforms for compliance auditing. Runs on Windows Server. | Free: 30-day trial/ Contact for pricing |
| N-able N-sight | Remote monitoring and management software with a risk intelligence module for protecting and reporting on PII. | none |
| Netwrix Auditor | Network security auditing software with configuration monitoring/ automated alerts/ and a Rest API. Offers detailed auditing and reporting/ hardware and device monitoring/ and automated remediation via scripts. Integrates with popular help desk platforms for automatic ticket creation. | Contact for pricing |
| Nessus | A vulnerability assessment tool for auditing/ configuration management/ and patch management. Provides a list of vulnerabilities on network devices and endpoints/ with customizable reports. Offers a free version (Nessus Essentials) and paid options for mid-sized and large organizations. | Free: Nessus Essentials/ Paid: Contact for pricing |
| Nmap | An open-source port scanner and network security scanner. Can discover hosts and find open ports vulnerable to attacks. Provides information on port status/ services/ and versions. Command-line utility with a GUI front-end called Zenmap. | Free |
6. Implement password management policies: To prevent the use of default passwords in the future, establish strict password management policies. This includes enforcing regular password changes, utilizing strong password complexity requirements, and educating users on the importance of creating unique and secure passwords.
By following these step-by-step instructions, readers can effectively conduct a security audit for default passwords on their Windows Server installations. This proactive approach will help enhance the overall security of their network and protect against potential unauthorized access.
Enforce strong password
To counteract this threat, it is essential to implement strategies and techniques that enhance the system’s security. One effective approach is to enforce strong password policies, requiring users to create passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Additionally, passwords should be changed regularly to maintain their effectiveness.
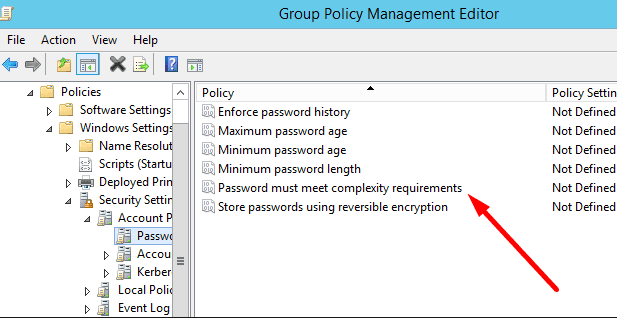
Robust account lockout policy
Another important measure to prevent brute-force attacks is to have a robust account lockout policy. This policy should automatically lock an account after a certain number of failed login attempts. By doing so, the server can protect itself from repeated attacks and potential unauthorized access.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Furthermore, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly enhance security by requiring users to provide additional verification, such as a fingerprint or a secondary code sent to their mobile device, when logging in. This additional layer of protection can prevent brute-force attacks from being successful even if the attacker manages to obtain the correct username and password combination.
Overall, protecting against brute-force attacks that exploit default passwords requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. By combining strong password policies, account lockout policies, MFA, and regular monitoring, server administrators can significantly reduce the risk of successful brute-force attacks and safeguard their systems.
In conclusion, it is essential for users to be aware of the default password in Windows Server to ensure their systems’ security. Implementing strong and unique passwords is critical to protect against unauthorized access and potential data breaches. Regularly changing the default password and employing additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication, can significantly enhance the server’s safety. It is advisable to follow best practices and stay updated with the latest security recommendations provided by Microsoft and other cybersecurity experts. By taking these precautions, users can better safeguard their Windows Server and prevent potential security vulnerabilities.
Relate Links :
Secret Reveal : What is the default administrator password for Windows Server 2016?
21-08-2023
John Weaver : Learn how to get back or reset the Windows Server 2016 default administrator password. Enhance security measures by...
How To Recover Data from A Hard Drive That Won't Boot: Ultimate Guide
22-02-2026
Ashley S. Miller : This article explains how to recover data from hard drive that wont boot by identifying common logical, firmware,...
Fixing "The Drive Where Windows Is Installed Is Locked" Error - Expert Guide
05-01-2024
Amanda J. Brook : Learn how to fix the "The drive where Windows is installed is locked" error and recover your important...
Step-by-Step Guide: Password Recovery Tool for Windows 2003 Server
21-08-2023
Ashley S. Miller : Introducing a powerful and free password recovery tool for Windows 2003 server. Learn its features and follow step-by-step...




